The following set of steps will show how to access a text selection and change it.
1.1. Pre-requirements
1.1.1 Creating a new action
In this example access to the Editor is made through an action as a plug-in point. To create an action we need derive AnAction.java class.
public class EditorIllustration extends AnAction {
}
1.1.2. Registering an action
To register the action we should add a corresponding attribute to the <actions> section of the plugin configuration file
plugin.xml
<actions>
<action id="EditorBasics.EditorIllustration" class="EditorIllustration" text="Editor Basics"
description="Illustrates how to plug an action in">
<add-to-group group-id="EditorPopupMenu" anchor="last"/>
</action>
If an action is registered in the group EditorPopupMenu, like the sample above shows, it will be available from the context menu when the focus is located in the editor.
1.1.3. Defining action's visibility
To determine conditions by which the action will be visible and available for being executed we need to override it's public void update(final AnActionEvent e) method.
public class EditorIllustration extends AnAction {
@Override
public void update(final AnActionEvent e) {
}
}
If we want to work with a selected part of the text, it's reasonable to make the action available only when the following requirements are met:
- There is a project open
- There is an instance of the Editor available
- There is a text selection in the Editor
Further steps will show how to check these conditions through obtaining instances of Project and Editor and how to set up a desired level of action's visibility.
1.2. Getting an instance of the Active Editor
A reference to an instance of the Editor can be obtained by calling CommonDataKeys.EDITOR,
obtaining a project reference is performed the same way CommonDataKeys.PROJECT.
public class EditorIllustration extends AnAction {
@Override
public void update(final AnActionEvent e) {
//Get required data keys
final Project project = e.getData(CommonDataKeys.PROJECT);
final Editor editor = e.getData(CommonDataKeys.EDITOR);
//Set visibility only in case of existing project and editor
e.getPresentation().setVisible((project != null && editor != null));
}
}
Note:
To access an Editor instance also can be used other ways:
If DataContext object is available
final Editor editor = CommonDataKeys.EDITOR.getData(context);If ActionEvent object is available
final Editor editor = actionEvent.getData(CommonDataKeys.EDITOR);
1.3. Obtaining a caret model and selection
After making sure we have a project open and an instance of the Editor we need to check if any selection is available and set action's visibility accordingly to these conditions.
SelectionModel
got from the Editor allows to do it by calling it's hasSelection() method.
Here's how our update(final AnActionEvent e) method should look like at the end:
public class EditorIllustration extends AnAction {
@Override
public void update(final AnActionEvent e) {
//Get required data keys
final Project project = e.getData(CommonDataKeys.PROJECT);
final Editor editor = e.getData(CommonDataKeys.EDITOR);
//Set visibility only in case of existing project and editor and if some text in the editor is selected
e.getPresentation().setVisible((project != null && editor != null
&& editor.getSelectionModel().hasSelection()));
}
}
Note: Editor allows to access different models of text representation. Model classes are located in editor subpackage of the editor-ui-api package and include:
- CaretModel.java,
- FoldingModel.java,
- IndentsModel.java,
- ScrollingModel.java,
- ScrollingModel.java,
- SoftWrapModel.java
1.4. Obtaining a Document
The action is visible and available now.
In order to make it do something we need to override it's
public void actionPerformed(final AnActionEvent anActionEvent) method.
public class EditorIllustration extends AnAction {
@Override
public void update(final AnActionEvent e) {
//code here
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(final AnActionEvent anActionEvent) {
}
}
To modify the text an instance of the Document needs to be accessed. Document represents the contents of a text file loaded into memory, and possibly opened in an IDEA text editor. The instance of a Document will be use later when a text replacement is performed. We also need to figure out where the selected part of the text is located.
@Override
public void actionPerformed(final AnActionEvent anActionEvent) {
//Get all the required data from data keys
final Editor editor = anActionEvent.getRequiredData(CommonDataKeys.EDITOR);
final Project project = anActionEvent.getRequiredData(CommonDataKeys.PROJECT);
//Access document, caret, and selection
final Document document = editor.getDocument();
final SelectionModel selectionModel = editor.getSelectionModel();
final int start = selectionModel.getSelectionStart();
final int end = selectionModel.getSelectionEnd();
}
1.5. Modifying text
Generally replacement can be done by calling
void replaceString(int startOffset, int endOffset, @NotNull CharSequence s); of the Document, however,
the operation of replacement must be executed safely, this means the Document must be locked and any changes should be performed under the write action. See the Threading Issues section to learn more about synchronization issues and changes safety on the IntelliJ Platform.
@Override
public void actionPerformed(final AnActionEvent anActionEvent) {
//Get all the required data from data keys
final Editor editor = anActionEvent.getRequiredData(CommonDataKeys.EDITOR);
final Project project = anActionEvent.getRequiredData(CommonDataKeys.PROJECT);
//Access document, caret, and selection
final Document document = editor.getDocument();
final SelectionModel selectionModel = editor.getSelectionModel();
final int start = selectionModel.getSelectionStart();
final int end = selectionModel.getSelectionEnd();
//New instance of Runnable to make a replacement
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
document.replaceString(start, end, "Replacement");
}
};
//Making the replacement
WriteCommandAction.runWriteCommandAction(project, runnable);
selectionModel.removeSelection();
}
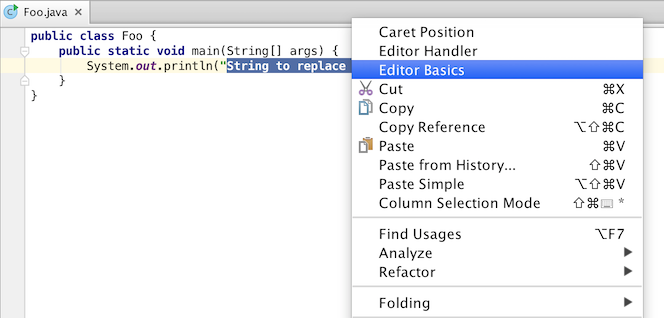
The source code is located in EditorIllustration.java. To see how text replacement works, check out Editor Basics plugin, make the project, and run it, then invoke the EditorIllustration action which is available in the context menu of the editor.